Computer Networking Overview
Computer Networking Overview
Computer
networking jobs
- 1. Client support – To solve the problem of the client in ISP (6 month course)
- 2. System Administration – To maintain the server
·
Windows (Course MCSE/MCSA)
·
LINUX Red hat (Course RHCE)
·
Free BSD
·
Sun Solaris
·
To Contact IT Bangladesh
- 3. Working in network core Layer & Distribution Layer.
·
CCNA
·
CCNP
·
CCSP
·
CCIE
·
To contact www.cisco.com or CISCO valley (Bangladesh)
History of
Networking or Internet
- 1. In 1958 SAGE- Sami Automated Ground Environment. This is used in Canada and USA for radar station for connects their computer.
- 2. In 1960- IBM-CTSS(Computable Time Sharing System) - Modem
- 3. In 1964 Dial up Service for American airlines.
- 4. In 1960 ARPANET (Advance Research Agency Network)- For US Military.
- 5. In 1971- E-Mail ARPANET for email.
- 6. In 1989 – Internet- DARPANET
Classification of
Network
Depend on Area Network
- 1. LAN
- 2. MAN
- 3. WAN
Depend on Function
Network
- 1. Peer TO Peer Network- In a central device, no server, all are equal, No Control.
- 2. Client Server Network- In a central device, server allow and the other server facilities.
- 3. Hybrid Network – Both of peer to peer network and Hybrid Network.
OSI (Open System
Interconnection) Model
- 1. OSI is created by International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 1974
- 2. OSI Model defines that how the network will work.
- 3. It allows various type of Hardware and software.
- 4. OSI Model is a logical model
- 5. There are seven Layers in OSI model. Top 3 is upper layers and bottom 4 is lower layers.
How it works…
UDP - User Datagram
Protocol
LLC –Logical link control
Layer 1 devices
- 1. Hub
- 2. Repeater
- 3. CSU/DSU
- 4. Media converter
ayer 2 devices
(work related to the Mac or the Hardware address.)
- 1. NIC
- 2. Bridge
- 3. Switch
- 4. Brouter
Layer 3 devices
- 1. Router
- 2. Brouter
Layer 4,5,6,7
devices
Gateway – It translates protocols and it used to connect two
separate networks that different communication protocols.
Depend on speed
there are three kind of Ethernet
- 1. 10 Mbps.
- 2. 100 Mbps (Fast Ethernet).
- 3. 1000 Mbps (Gigabit Ethernet).
Topology
Topology is the physical layout of network and how the
network can be seen from the top that call the topology. Network has both physical
and logical topology.
Physical topology
- 1. Bus topology – In a single link like Bus, the cable is coaxial cable, both end must have terminator.
- 2. Star topology – In a switch or Hub and this is look like Star.
- 3. Ring topology – look like ring and all computers is linking each other.
- 4. Mesh topology – Normally Use in wide area network and there have many paths which connect all computers if any one connection disconnects then the other one can connect by the other link.
- 5. Hybrid topology – This is combination of star and bus topology.
Logical topology
- 1. Logical Bus
- 2. Logical Ring
TCP/IP Layer
OSI
Model Layer TCP/IP Layer.
Wireless network
1.
Wi-Max( Worldwide
Interoperatibility Microwave Access) –
One tower which telecast the network. It give network to 60-70km.speed
70mbps,unlimited user
2.
Wifi – Three standards is
use 1.802.11a 2. 802.11b 3.802.11g.Give network 100 mitre. Speed 15+55mbps.User
limited.
3.
Bluetooth- In limited range
10 miter. Speed 20kbps.User limited.
IP address
There are 2 kind o IP address
- 1. Private
- 2. Public
Classification of
media
- 1. Cable media – 1. Twisted pair cable (UTP and STP 2. Coaxial cable 3. Fiber optic cable
- 2. Wireless media
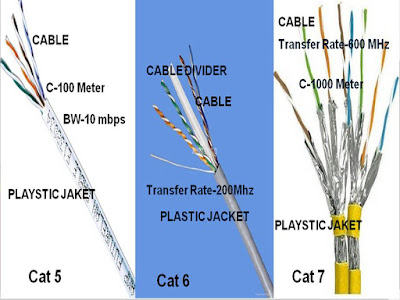
The diagram of UTP
cable and the STP cable is same characteristic as cat-5 cable
The coaxial cable
Fiber optic cable
- 1. Multimode fiber optic cable
- 2. Single mode fiber optic cable
There are two type
of connector in fiber optic cable
- SC connector
- ST connector
Wireless media
- 1. Micro wave transmission.
b. Satellite microwave – 50000 km
- 2. Radio wave transmission – Speed 1-10 mbps
- 3. Infrared transmission.
Ethernet cabling
- 1. Straight throw cable- Host to sw and router to sw
- 2. Cross throw cable- sw to sw, Hub to Hub, Host to Host, Hub to sw, Router direct to Host
- 3. Rolled cable- Is not used to connect any Ethernet connections together. IT USE TO
- CONNECT A HOST TO A ROUTER/SW CONSOLE SERIAL COMMUNICATION (COM PORT).
Modem
Modem – which convert the digital signal to the analogue
signal and also make the digital signal to the analogue signal.
1.
Internal modem
2.
External modem
a.
Cable modem – Download
speed 1.5 mbps
b.
DSL Modem – Download speed
– 1.8 mbps
c.
ADSL Modem – Download Speed
- 1.5 to 9 mbps
d.
EDGE (Enhanced data GSM
environment) Modem (USB wireless) - also call dialup modem, bandwidth 384 kbps,
this system is given by mobile company.
e.
GPRS (General packet radio
service) Modem (USB wireless) – speed 48 kbps
f.
CDMA (Code division
multiple access) Modem (USB wireless) – speed 153.6 kbps, citycell company give
the modem.
g.
EVDO (Evolution, Data only
or Evolution, data optimized) Modem (USB wireless) – This is a advance CDMA
technology. Speed- 2.4 mbps.























No comments